Background
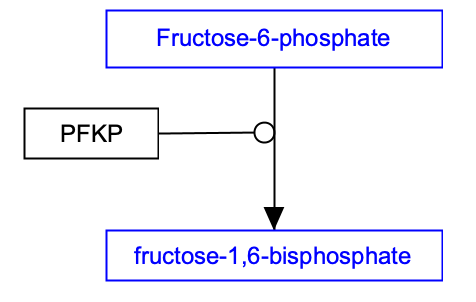
Metabolites are the reactants and products of the chemical reactions that occur in cells. Metabolites are not encoded in genes. Most commonly, they are extracted or synthesized from the foods we eat. Metabolites include molecules like lipids, sugars, cholesterol, and amino acids. Proteins called enzymes, catalyze the chemical reactions of metabolites. Understanding the relationship between Proteins (Gene Products) and Metabolites is critical to drawing metabolic pathways accurately. In the below example reaction, the PFKP node represents the enzyme phosphofructokinase, which converts the metabolite fructose-6-phosphate to the metabolite fructose-1,6-bisphosphate.
Challenge
The two most common types of molecules found in pathways are Gene Products and Metabolites. Which of the following is a Metabolite?